What Is Pendant Drop Surface Tension Measurement?
Pendant drop surface tension measurement is a technique used to determine the surface or interfacial tension of a liquid by analyzing the shape of a droplet suspended from the end of a syringe or capillary. The shape of the droplet, influenced by the balance between gravity and surface tension, is captured and fitted to the Young–Laplace equation to calculate the surface tension.
High Precision Results
Reliable and consistent surface/interfacial tension measurements, even with very small liquid samples.
Rapid and Accessible
Fast turnaround with secure digital reports, available anytime for easy review and sharing.
Non‑Destructive Testing
Preserves valuable or sensitive samples, ensuring accurate analysis without material loss.
Why Use Pendant Drop Surface Tension Measurement?
Pendant drop surface tension measurement is widely applied in research and industry to evaluate fluid behavior, surfactant efficiency, and interfacial interactions in formulations and coatings.
Surfactant Performance
Quantifies surface tension reduction to evaluate surfactant and additive effectiveness.
Formulation Optimization
Critical for developing stable coatings, adhesives, and emulsions by understanding interfacial behavior.
Quality Control and R&D
Supports both rapid QC and advanced research for product innovation and material development.
Covalent’s Capabilities Offer Pendant Drop Measurement
for Liquid Analysis and Interfacial Characterization

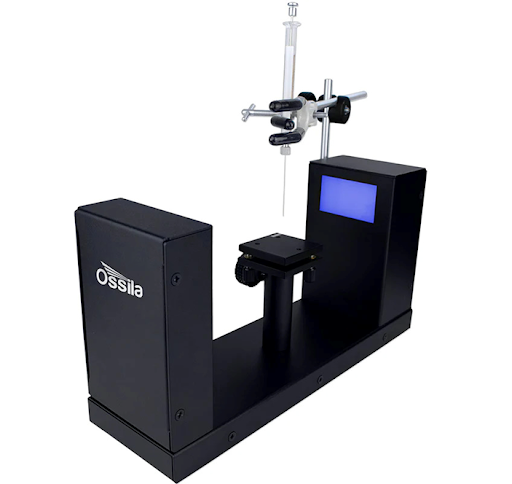
Working Principle
A pendant drop measurement works by suspending a backlit droplet from the tip of a needle or capillary and capturing its shape using a high-resolution camera. Automated image analysis software is used to extract the droplet’s and mathematically fit it using the Young–Laplace equation, which relates the shape of the drop to the surface or interfacial tension based on the balance between gravity and surface forces.
Equipment Used for Pendant Drop Surface Tension Measurement:
Ossila Contact Angle goniometer
- Angle range: 5° to 180°.
- Max measurement speed: 33 ms (30 fps).
- Maximum Camera Resolution 1920 x 1080.
Typical liquid droplets are on the order of microliters.

Key Differentiators
Strengths
- Rapid, inexpensive and sensitive assessment of surface tension.
Limitations
- Highly volatile liquids can be difficult to measure.

Unsure Whether Pendant Drop Measurement Is Right for You?
Learn more about using Pendant Drop measurement today.
Sample Information
Sample prep is straightforward, which makes this a fast and efficient testing option. To get the best results, liquid samples need to be clean, bubble and particle free. Covalent Metrology provides clear instructions to help you provide a clear sample, if materials need special handling, our team is ready to step in with expert support and custom solutions.
What we accept:
- Liquid sample.
- Hazardous liquids can be handled by moving the instrument into a fume hood.
- While typically the droplet is suspended in air, the drop can also be suspended in another liquid contained in a cuvette to measure the interfacial energy between 2 liquids.
Use Cases

Coatings/Paints/Inks
Measuring surface tension of formulations to optimize wetting, leveling, and substrate adhesion.

Pharmaceuticals & Biotech
Quantifying protein or surfactant effects on air–liquid and oil–water interfaces in drug formulations.

Cosmetics & Personal Care
Determining interfacial tension to design stable emulsions in creams, lotions, and shampoos.

Food & Beverage
Optimizing emulsifier concentration for stable emulsions and foams.

Chemical Manufacturing
Characterizing solvent mixtures and surfactants to control blending and separation behavior.
Semiconductor & Electronics Cleaning
Measuring surface tension of cleaning and rinsing solutions to control wetting and residue removal.

Polymer & Material Science
Determining interfacial tension between polymers and liquids for coating, adhesion, or composite design.

Environmental & Wastewater Analysis
Assessing surfactant contamination by monitoring changes in surface tension of aqueous samples.
Complementary Techniques
- Contact Angle: Measures surface wettability, complementing pendant drop by showing liquid-solid interaction.
- Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS): Identifies liquid chemicals, complementing pendant drop by linking interfacial behavior to molecular components.
Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)
Identifies and quantifies small organic molecules in mixtures. Explore
Why Choose Covalent for Your Pendant Drop Surface Tension Measurement Needs?
Frequently Asked Questions
Identifying the right test can be complex, but it doesn’t have to be complicated.
Here are some questions we are frequently asked.
What types of material can be tested using Pendant Drop?
Pendant drop measurements can be performed on a wide range of liquids, including pure fluids, solutions, and emulsions. Even volatile or hazardous liquids can be analyzed with special precautions.
How much sample is required for testing?
Only a small volume, typically a few tens of microliters, is needed to form the droplet for measurement.
What is the difference between surface tension and interfacial tension?
Surface tension refers to the force at the interface between a liquid and air, while interfacial tension describes the force at the boundary between two immiscible liquids or a liquid and a solid.
What kind of data or report will I receive?
The report typically includes measured surface or interfacial tension values, experimental conditions, and any calculated parameters, accompanied by images of the droplet profile.


