What Is X-ray Computed Tomography (Micro-CT)?
Micro-CT is a non-destructive method of visualizing and characterizing internal 3D structures of objects. It is capable of high-resolution X-ray reconstructions and allows for better understanding of the interior and exterior of a sample.
High-energy X-rays pass through slowly rotating samples about the X-ray source and the transmitted X-rays are projected onto a detector. This creates 2D X-ray images of the sample at various rotation angles. These 2D X-ray images are then compiled and reconstructed into a 3D model.
High‑Resolution
Imaging
Non‑destructive 2D/3D visualization of electronic components, battery layers, and hidden defects at micron scale.
Structural and Material Insights
Reveals density differences, porosity, and internal variations in composites and complex materials.
Non‑Invasive Biological Imaging
Visualizes internal structures of biological samples without damaging or altering them.
Why Use Micro-CT?
- Micro-CT is a non-destructive method of visualizing and characterizing internal 3D structures of objects without damaging the sample.
- It can be used in place of mechanical cross-sectioning when samples cannot be destroyed.
- Common uses of Micro-CT are in failure analysis of materials that can range from electronics to batteries to even plastics.
- Beneficial in semiconductor and battery industries.
- Beneficial for materials science industries.
- Micro-CT is also beneficial for biomedical industries.
Non‑Destructive Visualization
Reveals internal structures, defects, and layer measurements without cutting or damaging the sample.
Failure Analysis and Quality Control
Detects cracks, voids, shorting, and manufacturing defects across electronics, batteries, plastics, and composites.
Broad Industry Relevance
Trusted in semiconductors, batteries, biomedical, and materials science where precision imaging drives reliability.
Working Principle
Micro-CT works by using X-rays to look inside objects without cutting them open. The sample is placed between an X-ray source and a detector. As X-rays pass through the object, some are absorbed by dense or thick areas, while others pass through more easily. The detector captures many 2D images from different angles as either the sample or the X-ray source rotates. A computer then combines these images to create a detailed 3D model of the inside of the object, allowing you to see and measure features that would otherwise be hidden.
Equipment Used for Micro-CT:
Nordson Dage Quadra 7
- 30–160 kV, 20 W.
- 100 nm feature recognition.
- 7 MP flat panel digital detector.
- 30 fps framerate.
- 0–70° oblique angle view.
- 20 × 17.5” inspection area.
- Geometric magnification up to 2.5k× & total magnification up to 68k×.
- High Dynamic Range (HDR) enhancement software.
- X-Plane CT scanning of BGA solder balls.
- Dosage control for X-ray sensitive samples.

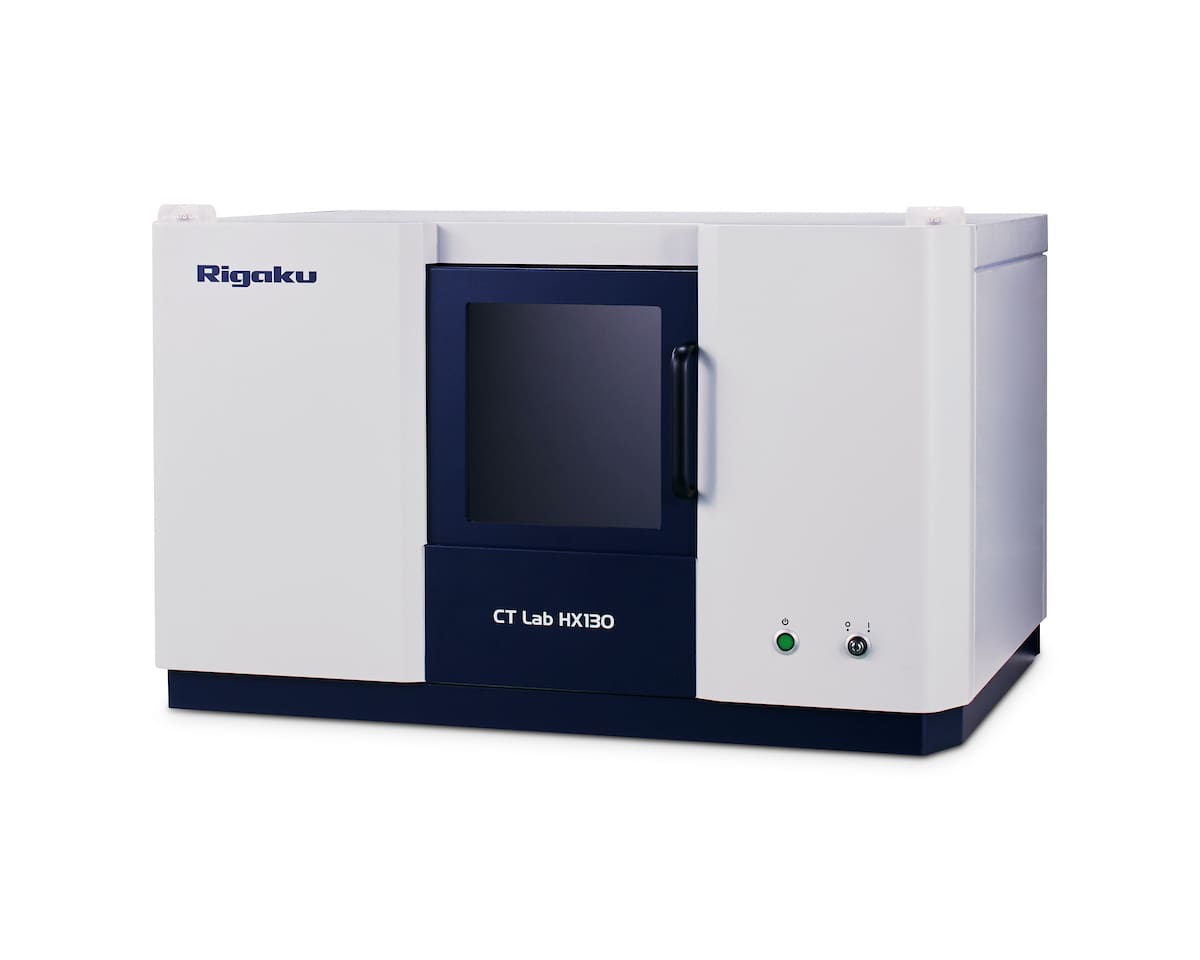
Rigaku CT Lab HX 130
- Field of View: 200 mm.
- Spatial Resolution Limit: 5 µm voxel resolution.
- X-ray Source Energy: 30 to 130 kV.
- X-ray Tube Current: up to 300 uA.

Key Differentiators
Micro‑CT gives unique structural insight without destroying the sample, but resolution and scan time depend on size and material.
Strengths
- Micro-CT is an invaluable tool for better visualizing the internal and external structure of a material. It is a non-destructive technique that can help identify internal features that would not be easily accessible without damaging the sample.
Limitations
- Micro-CT is a time-consuming technique and is limited by size. Only samples that are around 2mm in diameter allow for the best 2um resolution. Any samples with larger diameters will see a loss in resolution. Metallic artifacts may impact image clarity.

Unsure Whether Micro-CT Is Right for You?
Learn more about using Micro X-ray Computed Tomography services today.
Sample Information
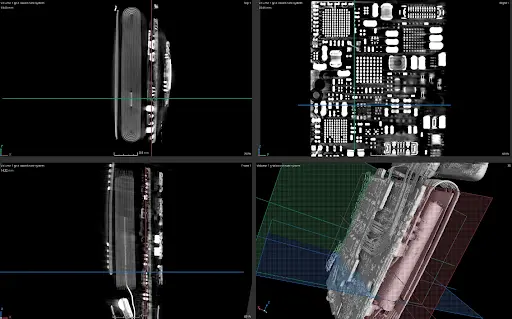
2D and 3D Micro-CT scan of a smartwatch.
What we accept:
We accept samples that are solid or can be securely held in place with hot glue to minimize vibrations during measurement. All samples must be stable in atmospheric conditions and can be up to a maximum of 5 cm in any dimension (x, y, or z) for Dage. For the HX130, we can take samples up to 130cm. For in-house analysis, samples are typically mounted using hot glue.
Use Cases
Semiconductor
Detects fatigue cracks, head‑in‑pillow defects, solder voids, and wire shorting without destructive sectioning. Supports process validation and reliability studies.

Battery
Visualizes layered structures, identifies internal shorting, broken units, and voids. Enables thickness measurements and failure analysis to improve safety and performance.

Biomedical
Non‑destructive imaging of implants and biological samples to reveal internal structures, contamination, or porosity. Ensures compliance, quality, and reliability.
Complementary Techniques
- 2D X‑ray Imaging: Quick overview method for detecting cracks, voids, and density variations. Complements Micro‑CT’s high‑resolution 3D reconstructions.
- Focused Ion Beam (FIB): Prepares site‑specific cross‑sections at the nanoscale, giving precise validation of features first identified by Micro‑CT.
- Mechanical Cross‑Section: Reveals internal structures through physical sectioning. When paired with Micro‑CT, it provides direct validation of non‑destructive imaging.
- Optical Microscopy: Enables visual inspection of polished sections, offering a cost‑effective complement to the 3D insights of Micro‑CT.
- Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM): Delivers high‑resolution imaging of exposed cross‑sections for detailed surface and defect analysis beyond CT limits.
Mechanical Cross-Section Analysis (X-Section)
Uncovers microstructures and defects causing performance issues. Explore
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
Images surface topography and composition with electrons. Explore
Why Choose Covalent for Your Micro-CT Needs?
Frequently Asked Questions
Identifying the right test can be complex, but it doesn’t have to be complicated.
Here are some questions we are frequently asked.
What types of materials or parts can be scanned with Micro-CT
Samples need to be solid or able to be held in place with hot glue so as to limit vibrations during measurement.
What are the main business applications of Micro-CT?
Micro-CT is often used as a non-destructive visualization method to look at internal features or detect potential failures within a sample.
What size samples can be scanned?
Samples can be up to 5cm maximum in either x, y, and z parameters. Larger samples can be either used in the HX130 (at lower resolution) or sent out to partner labs that can accommodate larger/denser samples.
How accurate are the measurements from Micro-CT scans?
Currently, measurements have an error of 3%.
How long does a typical Micro-CT scan take?
A typical Micro-CT scan takes 2-3 hours. Depending on the resolution needs, the scans can be taken for shorter periods of time, which will decrease the resolution or longer periods of time, which will increase the resolution.
What kind of analysis or reporting is provided after scanning?
A free viewer is provided where clients can have access to the full 3D reconstruction and allows them to go slice by slice through their scanned material. A report is also provided, which can include any failures found or measurements that the client requested.