What Is Infra-Red Thermography (IRT)?
Infra-Red Thermography (IRT) is a non-destructive testing technique that visualizes temperature variations on a material’s surface to reveal hidden defects and assess thermal performance. By capturing infrared radiation and converting it into detailed thermal images, IRT enables precise, real-time inspection of electronic components, materials, and devices under operation. Ideal for detecting hotspots, delaminations, and other anomalies, it provides a fast, contact-free way to ensure reliability and quality across applications.
For design: Infrared Thermography (IRT) non-destructively visualizes surface temperatures to reveal defects, hotspots, and ensure reliability.
Dual-Mode Imaging
Works in passive and active modes for surface and subsurface defect detection.
High Sensitivity
Detects minute temperature variations (<0.05 °C) and fine spatial details (<50 µm).
Real-Time and
Non-Contact
Enables full-field thermal imaging of live or sensitive systems safely.
Why Use IRT?
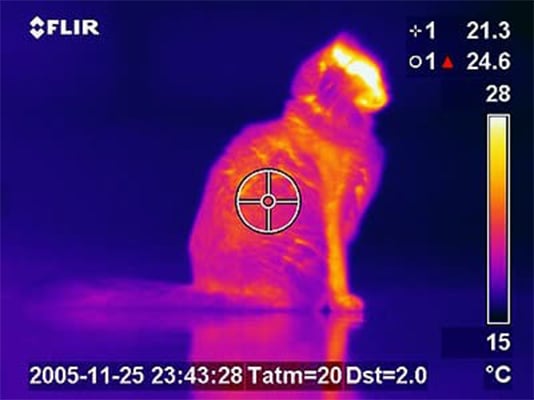
Infra-Red thermography analysis works on the fact that every object above absolute 0 Kelvin emits infrared radiation. Although the intensity of this radiation depends on the object’s temperature and surface properties, Infra-Red Detectors can capture this radiation very accurately by using thermal sensor arrays.
The thermal imager produces a thermogram by detecting emitted radiation and applying emissivity corrections. Software is then able to measure, analyze, and highlight temperature anomalies.
There are two types of analysis that Infra-Red Thermography can provide:
- Passive Thermography: Measures the object’s natural temperature differences (e.g., electronics under a load).
- Active Thermography: Uses external thermal stimulus, like hot air, flash lamp, or laser, to enhance contrast and detect sub-surface features.
Early Defect Detection
Reveals thermal fatigue, delamination, and cracks invisible to optical tools.
Improved Reliability
Identifies heat anomalies early to prevent failures and ensure consistency.
Wide Industry Use
Ideal for semiconductors, batteries, solar panels, and medical components.
Working Principle
Infra-Red Thermography (IRT) works on the principle that all objects above absolute zero emit infrared radiation proportional to their temperature. A thermal camera detects this radiation using sensitive infrared sensors and converts it into a visual image called a thermogram, where different colors represent temperature variations. By analyzing these thermal patterns, IRT reveals surface and near-surface temperature differences that indicate material properties or hidden defects. In passive mode, it captures natural heat emissions, while in active mode, an external heat source such as a laser or flash lamp enhances contrast, making subsurface irregularities easier to detect.
Equipment Used for IRT:
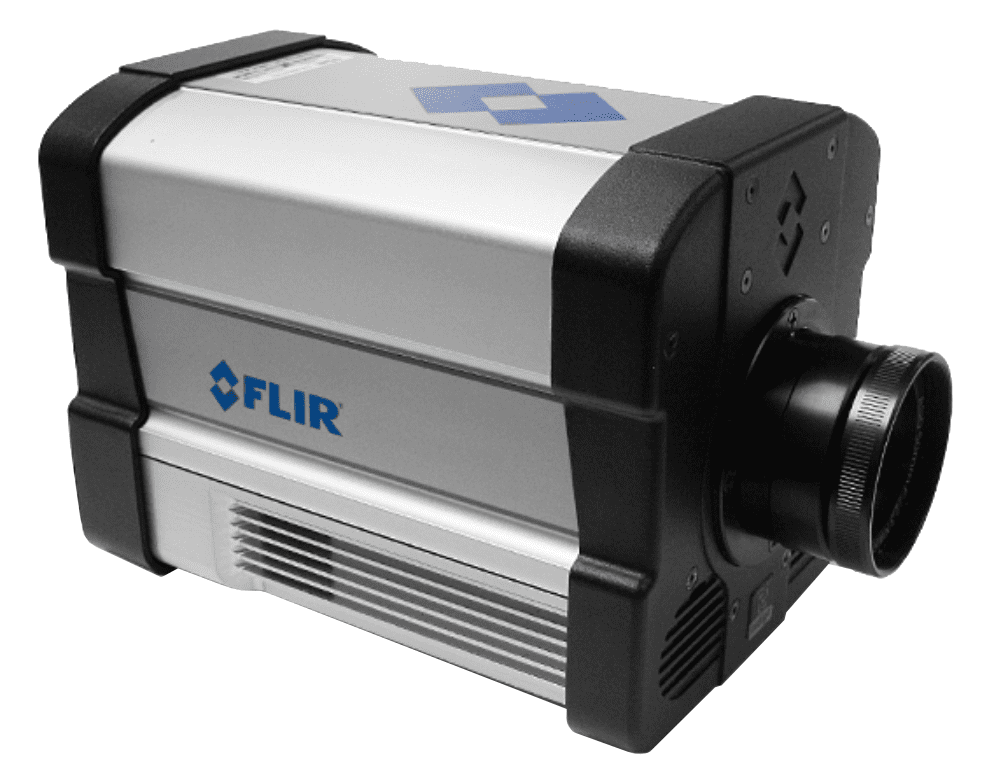
Covalent uses the FLIR ThermoVision SC6000 IR camera for advanced Infra-Red Thermography inspections. This high-performance system enables precise, non-contact thermal imaging for detecting surface and subsurface temperature variations across a wide range of materials and devices. It is ideal for applications in microelectronics, solar panels, energy storage components, and other high-value or sensitive assemblies.
FLIR ThermoVision SC6000 IR
Key Features:
- Detector Type: Indium Antimonide (InSb) for high-sensitivity thermal detection.
- Spectral Range: 3.0 to 5.0 microns for accurate infrared capture.
- Temperature Range: -25 to +500 °C to accommodate diverse applications.
- Temperature Sensitivity: As low as 0.018 °C for detecting subtle variations.
- Adjustable Frame Rate: 0.0015 Hz to 126 Hz for real-time and dynamic thermal imaging.

Key Differentiators
Capabilities:
- Detects surface and near-subsurface temperature variations with high thermal sensitivity (<0.05°C).
- Provides real-time, full-field thermal imaging for live and static systems.
- Supports both passive (natural heat emission) and active (externally stimulated) thermography modes.
- Compatible with a wide range of materials, including semiconductors, polymers, composites, coatings, and electronic assemblies.
- Enables precise localization of thermal anomalies such as hotspots, delamination, and cracks.
Specifications:
- Thermal Resolution: <0.05°C (depending on setup and optics).
- Spatial Resolution: Up to <50 µm, depending on detector and optical configuration.
- Excitation Sources (for active IRT): Flash lamp, laser, or hot air for enhanced defect visibility.
- Data Output: Quantitative thermograms with emissivity correction and temperature mapping.
- Sample Conditions: Ideal for non-contact testing; may require matte coating for reflective surfaces.
Strengths
- It is a non-contact and non-destructive testing method.
- Provides real-time thermal imaging inspection.
- It is safe to use in hazardous and high-voltage environments.
Limitations
- Surface emissivity due to finish or color impacts readings.
- Air currents, reflections, and ambient heat sources affect accuracy.
- Sub-surface detection depends on thermal diffusivity and excitation methods.
- Spatial Resolution is independent of camera optics and detector pixel size.

Sample Information
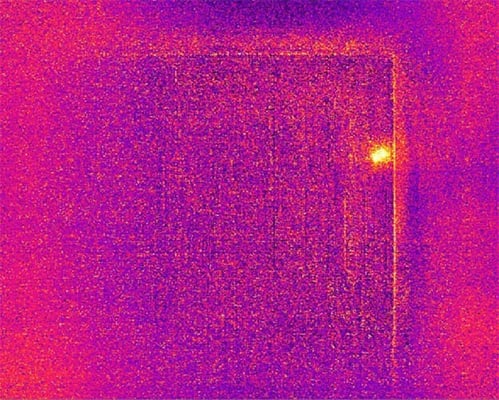
These outputs are essential for identifying thermal irregularities, assessing material performance, and supporting non-destructive failure analysis.
IRT image showing a hot spot in upper right corner of a flip-chip die: differential/subtraction mode.
What we accept:
- Must have an accessible, clean surface for thermal imaging.
- Flat or slightly contoured surfaces yield the most reliable data.
- Highly reflective or low-emissivity materials (e.g., polished metals) should be coated with a temporary matte finish to improve emissivity.
- Samples should be stable under mild thermal excitation (if active thermography is used).
- Height clearance must accommodate the optical setup of the thermal camera.
- Samples requiring fine probing or electrical contacts are not suitable for thermal imaging.
Not sure if your sample qualifies? Talk to our experts for prep guidance and optimal data quality.
Use Cases
Electronics & Semiconductor
Detect hot spots, thermal fatigue, and abnormal heating in integrated circuits, PCBs, and semiconductor devices without disassembly.

Battery & Energy Storage
Identify hotspots, delamination, or defects in electrodes, cells, and packs to ensure safety and performance.

Medical Devices & Biotech
Assess thermal behavior in implantable devices, sensors, and thin films, ensuring uniformity and detecting hidden defects.

Solar & Photovoltaics
Locate cracks, delamination, and degradation in solar panels and modules, improving efficiency and reliability.

Materials Science & Manufacturing
Examine polymers, composites, coatings, and laminates for thermal uniformity, internal defects, or material inconsistencies.
Complementary Techniques
- Decapsulation: Allows direct inspection of die surfaces, bond pads, and failure sites.
- Electrical Testing: Correlates thermal behavior with performance issues like shorts or opens.
- Mechanical Cross-Sectioning: Exposes internal layers to inspect material defects, metallization cracks, and delamination.
- Optical Microscopy: Examines surface-level defects and material integrity.
- Scanning Acoustic Microscopy (SAM): Maps internal features and detects delaminations, voids, and cracks.
- X-Ray Imaging : Reveals internal structures, solder joints, bond wires, and hidden defects.
Mechanical Cross-Section Analysis (X-Section)
Uncovers microstructures and defects causing performance issues. Explore
Scanning Acoustic Microscopy (SAM)
Locates internal flaws like cracks, voids, and delamination. Explore
Why Choose Covalent for Your IRT Needs?
Frequently Asked Questions
Identifying the right test can be complex, but it doesn’t have to be complicated.
Here are some questions we frequently get asked:
What is Infrared Thermography (IRT)?
Infrared thermography is a non-destructive testing method that captures and visualizes the heat patterns and distribution of an object’s surface. It easily allows for visualization of temperature changes across a part or a device. Our infrared inspection services stand out in their usefulness in detecting hidden defects, understanding material performances, as well we monitoring thermal events during operation.
What types of samples can be analyzed through IRT thermal imaging inspection?
Infrared inspection services are suitable for a wide variety of materials such as semiconductors and electronic devices, as well as polymers and composites. It also works very well for thin films and coatings, adhesive bonds, and laminates. It is even great for batteries and energy storage components. It is important to consider surface emissivity and geometry of each material, respectively, to ensure accurate results.
What are the common applications of IRT at Covalent?
At Covalent, we use thermal imaging inspection services primarily for Failure Analysis, such as hot spot detection in Integrated Circuits or solar panels.
How well can IRT detect subsurface defects?
Even though thermal imaging inspection is primarily surface-sensitive, active thermography- using an external heat sourc-allows for enhanced visibility of subsurface defects. The effective depth depends on the material’s thermal diffusivity, thickness of layers, and type of excitation, such s flash, lock-in, and pulse.
What are the spatial and thermal resolutions?
Covalent’s infrared inspection services stand out with their spatial resolution that can reach <50 µm, depending on optics, and their thermal sensitivity, which is typically <0.05°C. This allows for the detection of even the smallest temperature changes.
What is the difference between active and passive thermography?
Passive IRT relies on naturally occurring temperature differences, such as a powered device, while active IRT uses external stimulation, such as a flash lamp, laser, or heat source, to induce the thermal contrast, which is ideal for defect detection in otherwise uniform materials.
Do I need to apply a coating to my sample?
Only if your sample has very low emissivity (e.g., polished metals) or a highly reflective surface.
If that is the case, we suggest using a temporary matte coating to improve emissivity and image quality.Can IRT be used on live electronic devices?
Yes. Covalent’s infrared inspection services support real-time imaging of operating devices.
What are the limitations of IRT?
There are several factors that may reduce accuracy, such as the object’s poor surface properties or environmental factors, such as air flow and ambient light will also affect the readings. Deeper defects may not be visible without active methods. However, Covalent’s team accounts for these factors with careful calibration and setup.





