What Is Nano-Scratch?
At a constant normal load, nano-scratch tests the coefficient of friction and scratch hardness, which are important for characterizing a material’s resistance to scratch and wear.
A coating scratch test can characterize interfacial adhesion at a progressive, linear, normal load, determining how well a coating adheres to a substrate.
Precision Measurement
High force and displacement resolution for accurate results.
Real-World Simulation
Mimics everyday handling of materials for relevant testing.
Mechanical and Surface Properties
Evaluates friction, scratch hardness, and adhesion of thin coatings.
Why Use Nano-Scratch?
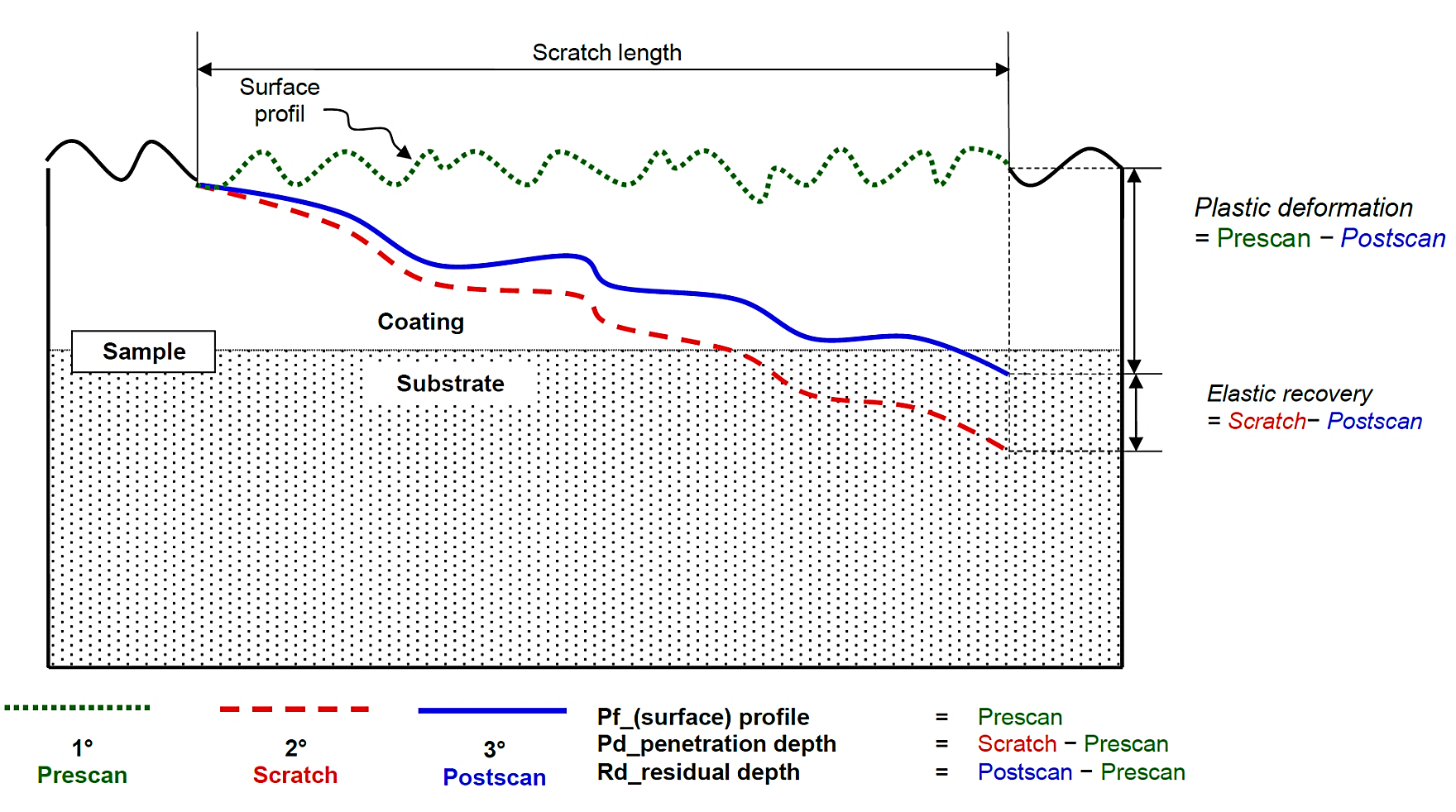
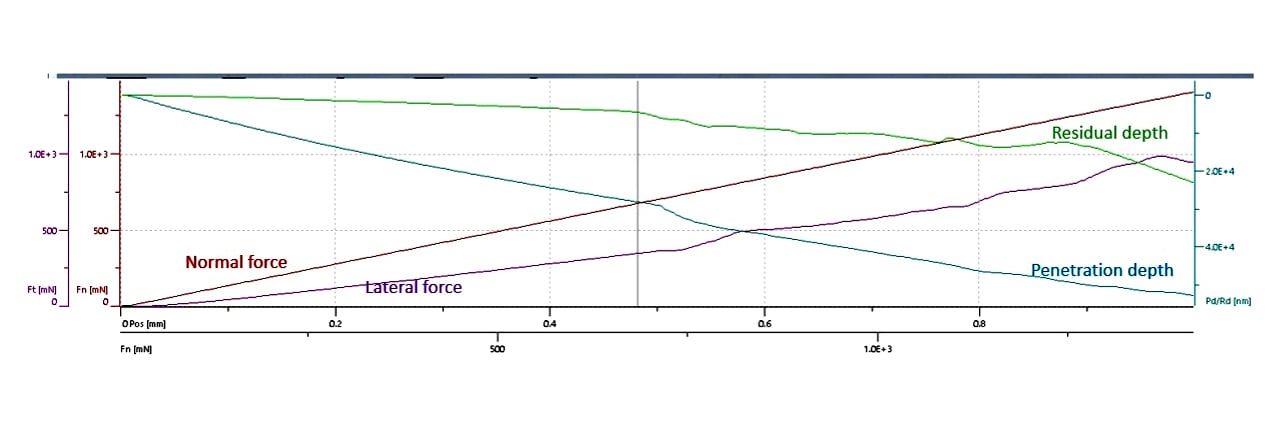
Nano-Scratch measurement output is the lateral force and the indenter displacement. Our nano-scratch tester operates in a 3-pass mode. As seen in the image below, in the 1st pass, the topographic line profile of the surface can be probed using very low force. In the 2nd pass, the nano-scratch testing function is applied. Finally, the 3rd pass measures the scratch profile’s topography to determine the coating material’s permanent plastic deformation and elastic recovery.
Depth Resolution
The micro scratch testing has a depth resolution of 0.11 nm and a load resolution of 0.01 micro-newton.
Lateral resolution
This depends on the contact depth of the indenter.
Working Principle
Our coating scratch test stands out in its resolution in force and displacement. It allows you to measure the coefficient of friction, scratch hardness, and interfacial adhesion of thin coatings. These measurements are important for characterizing the mechanical properties used in optical components, smartphone glass, and wafer coatings. Coating scratch tests provide well-controlled studies that can simulate real-world handling of materials. They offer more profound insights into designing new scratch-resistant coating materials.
Equipment Used for Nano-Scratch:
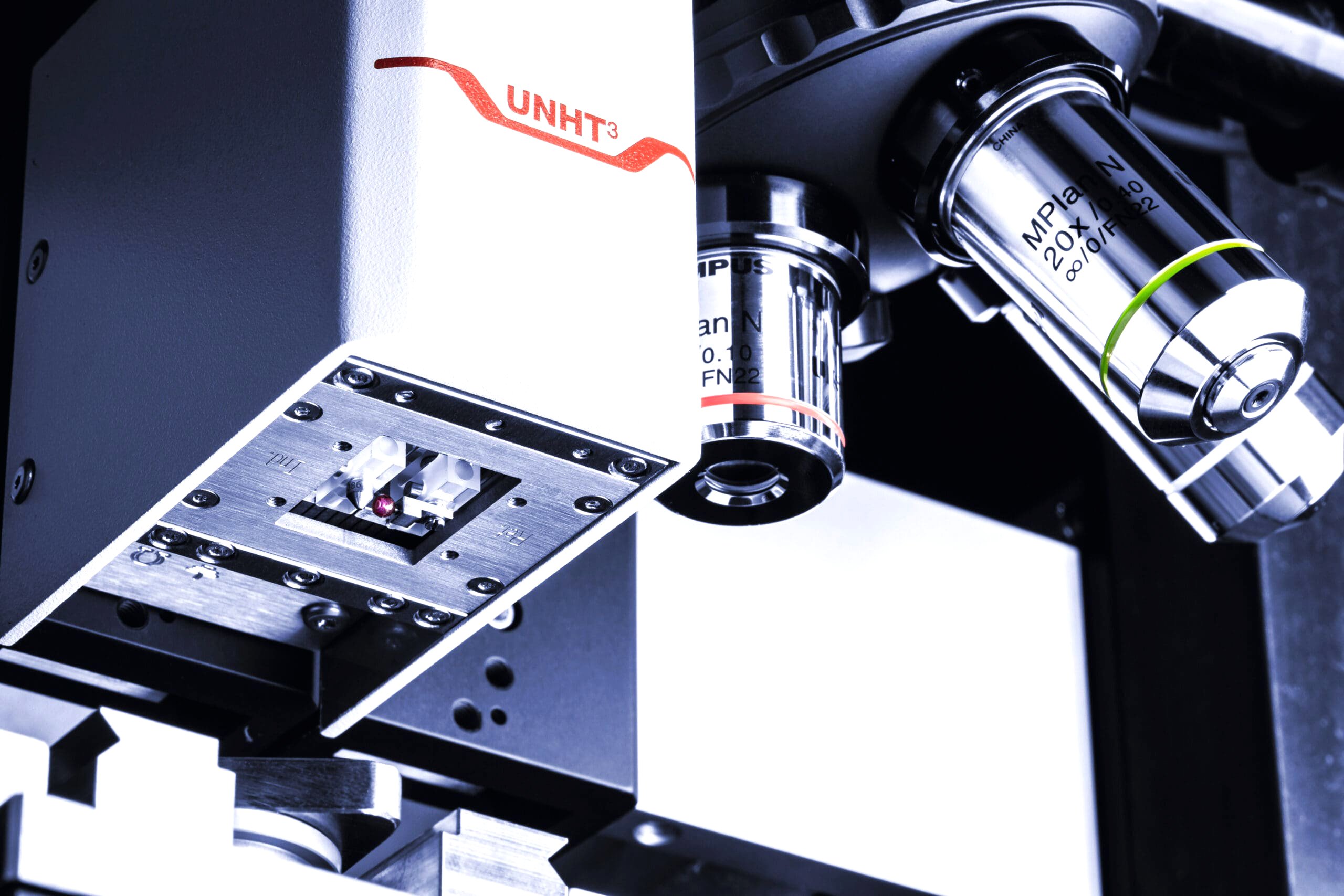
Anton Paar UNHT3 Ultra Nanoindentation Tester
- Multiple Nanomechanical Testing Heads:
- UNHT3: Ultra Nanoindentation Tester
Normal Load Range: 10 μN to 100 mN. - NST3: Nano-scratch Tester
Normal Load Range: 10 mN to 1 N.
- UNHT3: Ultra Nanoindentation Tester
- Depth Range: 10 nm to 100 μm.
- Acoustic enclosure with anti-vibration table.
- Heated stage.
- Integrated optical video microscopes for synchronized panoramic imaging during force measurement.
- Long-term thermal stability for elevated-temperature analysis.
| Maximum load [mN] | 1000 |
| Load resolution [μN] | 0.01 |
| Maximum friction force [mN] | 1000 |
| Friction force resolution [μN] | 1 |
| Maximum depth [μm] | 600 |
| Depth resolution [nm] | 0.1 |
| Scratch speed [mm/min] | 0.1 to 600 |

Key Differentiators
Simulates real-world mechanical wear at the nanoscale to measure adhesion, friction, and scratch resistance of thin coatings.
Strengths
- High force and displacement resolution.
- Mimics every everyday handling of materials.
- Measures the coefficient of friction, scratch hardness, and interfacial adhesion of thin coatings.
Limitations
- Does not work with concave surfaces.
- Cannot provide accuracy of 5 microns or less.
- Soft materials are unsuitable for internal instrumentation.
- High surface roughness induces variations in results.

Unsure Whether Nano-Scratch Is Right for You?
Covalent's expert team helps understand your requirements and designs a testing plan made for your needs.
Use Cases

Battery Materials
Adhesion strength of laminate electrodes on current collectors.
Semiconductor
Adhesion strength of passivation layers.
MEMS
Gliding friction of anti-stiction coatings.

Consumer Electronics
Scratch durability of hard plastic coatings, scratch resistance of DLC coatings, and scratch hardness of chemically tempered glass.

Lubricants
Shear strength of tribo-films.
Complementary Techniques
- Indentation: In addition to scratching, indentation can measure the hardness differences between the coating and substrate and their influence on scratch failure modes.
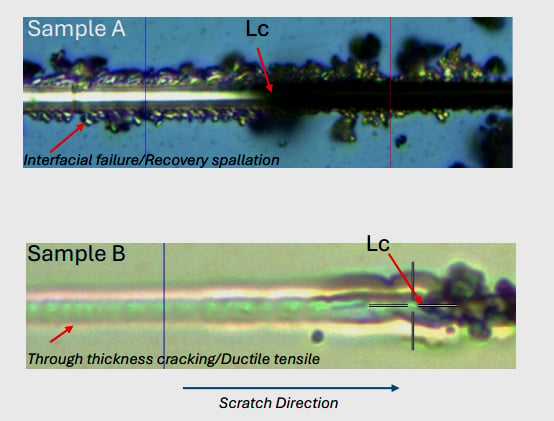
- Optical Microscopy or Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM): We recommend using optical microscopy or SEM (Scanning Electron Microscopy) to visualize the scratch.
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
Images surface topography and composition with electrons. Explore
Why Choose Covalent for Your Nano-Scratch Needs?
Covalent provides top-of-the-line micro scratch testers equipped with an optical microscope that captures panoramic images of each scratch and then correlates failure modes imaged optically with the lateral force scratch output. Typically, we test five scratches and report the average scratch hardness or critical load for interfacial coating adhesion.
Frequently Asked Questions
Identifying the right test can be complex, but it doesn’t have to be complicated.
Here are some questions we are frequently asked.
What is Nano-scratch testing?
Nano-scratch testing is a surface analysis method that measures lateral force and scratch hardness using a sharp tip that slides across a sample.
How does Nano-scratch testing work?
A test is performed in three phases: scanning the surface profile, the actual scratch that is made under constant or progressively increasing normal load, and a final scan to measure the residual scratch depth and elastic recovery.
What materials can be tested?
Nano-scratch works best on solid, flat samples such as metals, ceramics, and plastics.
What insights can Nano-scratch provide?
It may determine the coefficient of friction, scratch hardness, and the critical loads for coating adhesion.