What Is Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy (ICP-OES)?
Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy (ICP-OES), also called ICP Atomic Emission Spectroscopy (ICP-AES), measures the elemental composition of liquids or digested solid samples.
In ICP-OES, the atoms in an argon plasma are energized, causing them to emit light at element-specific wavelengths, each wavelength indicating a unique fingerprint.
ICP‑OES supports detection at the parts‑per‑billion (ppb) level. At Covalent, every method is built with rigorous control over sample prep, calibration, and spectral interpretation to ensure the data aligns with your decision-making needs.
Multi‑Element Speed
Screens and quantifies dozens of elements in a single scan, with rapid throughput for both research and QA workflows.
High Sensitivity
Detects trace metals down to low parts‑per‑billion while maintaining linear response across wide concentration ranges.
Matrix Flexibility
Tolerates complex mixtures (biological, environmental, industrial) with robust digestion workflows that preserve accuracy.
Why Use ICP-OES?
ICP‑OES is an excellent choice for quick, economical trace elemental analysis, supporting projects that demand accurate multi‑element quantification without the complexity of higher‑sensitivity techniques.
It is ideally suited for trace metal detection, elemental impurity analysis, leaching studies, and stoichiometry determination, enabling reliable insights across research, manufacturing, and quality control workflows.
With excellent sensitivity, broad linear range, and robust matrix tolerance, ICP‑OES delivers fast, defensible results even for complex sample types, making it a practical and efficient tool for most elemental testing requirements.
Analytical Breadth
Handles trace to bulk concentrations (ppb to ppm), enabling impurity detection, stoichiometry validation, and compliance checks.
Application Versatility
Supports industries from semiconductors and energy storage to pharmaceuticals, food, and mining, with proven regulatory alignment.
Workflow Integration
Compatible with complementary methods (ICP‑MS, combustion, microwave digestion) to extend analytical coverage and confidence.
Working Principle
ICP-OES translates emitted light into quantitative elemental data. A liquid or digested solid sample is nebulized into a fine aerosol and then injected into a high-temperature argon plasma.
Inside the plasma, atoms emit photons as electrons return to the ground state. A detector captures these emissions, correlating wavelength intensity to elemental abundance.
Covalent’s platform is engineered to deliver accurate elemental profiles from even difficult sample matrices.
Equipment Used for ICP-OES:
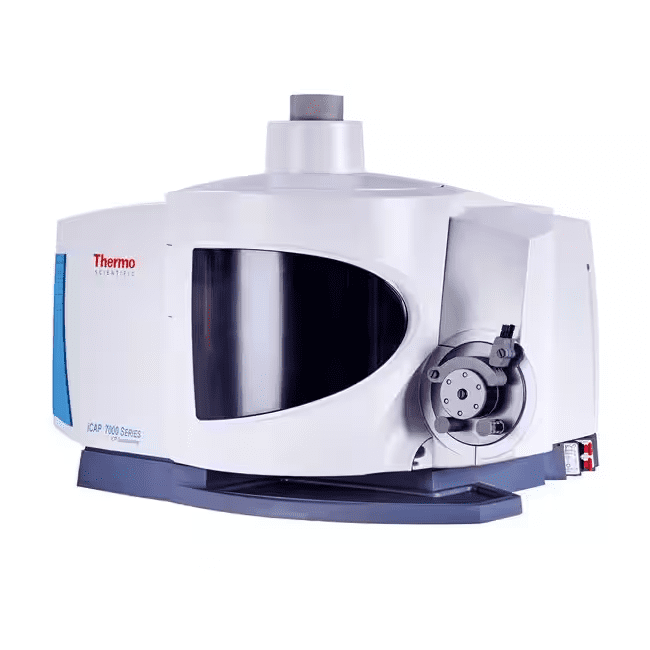
Covalent’s ICP-OES workflow is powered by the ThermoFisher Scientific iCAP-7400 Duo, configured with:
ThermoFisher Scientific iCAP-7400 Duo
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Spectrometer | Wavelength range from 166 to 847 nm, supporting flexible detection across most elements |
| Detector | Charge Injection Device (CID86) providing precise, stable spectral detection over wide concentration ranges |
| Optics | Thermostatically controlled polychromator (stability within 0.1 °C) with optimized optical design for consistent resolution and accuracy |
| Sample Introduction | Compatible with diverse sample matrices through robust nebulizer systems and flexible accessories |
| Automation | Autosampler support for reliable, unattended, high-throughput operation |
| Prep Support | Sample preparation workflows including microwave digestion for challenging solids, oils, and reactive materials |
This configuration is ideally suited for trace metals analysis, multi‑element scans, and high‑throughput projects. It delivers low detection limits (10 to 50 ng/L), broad spectral coverage (166 to 847 nm), and repeatable performance across complex sample types.

Key Differentiators
ICP-OES is built for rapid, high-precision multi-element analysis. Our configuration supports both exploratory research and routine QA programs.
ICP‑OES detects trace and bulk elemental concentrations (ppb to ppm), enabling multi‑element profiling in complex mixtures and revealing impurities, leachates, and major constituents. Compatible with aqueous solutions, digested solids, alloys, polymers, oils, ceramics, biomaterials, pharmaceuticals, and minerals, ICP‑OES adapts to nearly any plasma‑ready matrix.
ICP-OES vs ICP-MS
Both techniques rely on plasma excitation but diverge in detection mode.
| Parameter | ICP-OES | ICP-MS |
|---|---|---|
| Detection | Optical emission spectroscopy | Mass spectrometry |
| Sensitivity | Moderate (ppb) | High (ppt) |
| Isotopic Analysis | Not available | Available |
| Matrix Tolerance | High | Lower |
| Throughput | High (faster setup and analysis) | Slower due to prep and interference control |
When to Choose ICP-OES:
- You need fast, multi-element screening.
- Sample prep time is limited.
- Matrix interference is a concern.
- Isotopic or ultra-trace analysis is not required.
Get in touch with our experts to determine the best-fit technique for your matrix, detection thresholds, and reporting requirements.
Strengths
- Detects elements at ppb concentrations.
- Simultaneous multi-element scans.
- Linear dynamic range across orders of magnitude.
- Minimal sample mass required.
- Compatible with aggressive digestion workflows.
Limitations
- Requires samples in solution form.
- Cannot resolve isotopes or molecular structures.
- Surface and depth profiling are not supported.
- Susceptible to matrix effects if not calibrated correctly.
Covalent addresses these challenges through matrix-matched standards, validated digestion workflows, and QA-verified calibration.

Unsure Whether ICP-OES Is Right for You?
Learn more about using Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy testing services today.
Sample Information
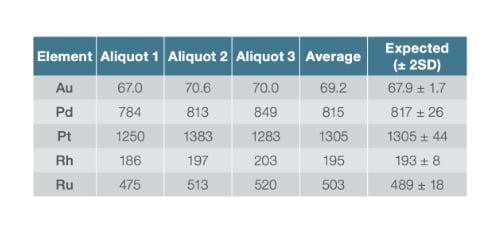
The example below highlights how ICP‑OES delivers precise, repeatable results when quantifying Platinum Group Metals (PGMs) such as Au, Pd, Pt, Rh, and Ru. These elements are critical in advanced technologies and manufacturing, and accurate measurement is essential to ensure quality and performance.
- Excellent agreement between replicate measurements across three aliquots.
- High precision, with results closely matching the expected reference values.
- Reliable quantification of precious metals, even at elevated concentrations.
What we accept:
- Liquids and aqueous extracts.
- Acid-digested solids.
- Metals, ceramics, polymers, and composites.
- Complex bulk mixtures or residues.
Preparation Requirements:
- The sample must be plasma-compatible.
- Acid digestion, microwave digestion, or combustion may be required.
- Only milligram-scale quantities needed.
Need support with sample prep or method setup? Our experts are ready to assist.
Use Cases
Semiconductor & Microelectronics
Monitor trace metals in wafers, resists, and components to protect device integrity.

Pharmaceutical / Biotech / Clinical Labs
Detect elemental impurities in APIs, excipients, and biologics for regulatory compliance.

Energy Storage & Power Generation
Analyze electrolytes, electrodes, and degradation products in batteries and fuel cells.

Environmental Monitoring & Compliance
Measure trace metals in water, soils, and effluents to meet safety standards.

Food / Agriculture / Nutrition Science
Profile nutrients and contaminants in consumables, fertilizers, and animal feeds.

Geology / Mining / Metallurgy
Characterize ores, validate alloys, and track elemental composition during extraction and refining.
Complementary Techniques
ICP-OES is the best fit for the complete story when paired with other deeper and broader-spectrum techniques:
- Combustion Analysis / Inert Gas Fusion: Atmospherics (C, H, N, O, S) quantification.
- ICP-MS: Higher sensitivity, isotopic analysis.
- Ion Chromatography: Halides and organic acids not detected by ICP-OES.
- SEM-EDS: Surface imaging, low-concentration elemental ID.
- XPS: Elemental + bonding environment, surface analysis.
- XRF: Non-destructive solid-state elemental analysis.
Every ICP-OES program at Covalent is engineered for purpose, built to power your compliance, innovation, and production goals.
Energy Dispersive X-ray Fluorescence (EDXRF)
Quick, non-destructive material composition & thickness analysis. Explore
Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS)
Measures trace elements with high accuracy. Explore
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
Images surface topography and composition with electrons. Explore
X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
Measures surface elemental composition and chemical states. Explore
Why Choose Covalent for Your ICP-OES Needs ?
Every ICP-OES program at Covalent is engineered for purpose, built to power your compliance, innovation, and production goals.
Our services are:
- Methodologically rigorous: We offer microwave digestion, matrix-matched calibration, and controlled combustion workflows tailored to each sample’s chemistry and goal.
- Operationally fast: Our iCAP‑7400 system is optimized for high‑throughput without compromising sensitivity. Clients get rapid turnarounds without sacrificing data quality.
- Strategically aligned: We consult with you to define reporting thresholds, compliance targets, and process inputs, ensuring your data is accurate and actionable.
At every stage, from formulation validation to compliance documentation, Covalent delivers data that drives confident decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Identifying the right test can be complex, but it doesn’t have to be complicated.
Here are some questions we are frequently asked.
When should I use ICP-OES instead of ICP-MS or other elemental analysis methods?
ICP‑OES is the better choice when samples have a complex matrix, analyte concentrations are relatively high, and you don’t need isotopic analysis.
What are the detection limits and accuracy levels achievable with ICP-OES at Covalent Metrology?
At Covalent, ICP‑OES can achieve detection limits in the single‑digit parts‑per‑billion range, with relative standard deviation (RSD) typically under 3%.
How is a sample prepared for ICP-OES testing, and what are the minimum volume or concentration requirements?
Solid samples are usually digested or dissolved into a dilute acidic solution. Liquid samples are often diluted in acid, though in many cases they can be analyzed as received.
What kind of data does ICP-OES provide, and how is it typically used in research or quality control?
ICP‑OES provides calibrated, quantitative elemental composition for most elements (excluding atmospheric gases, noble gases, and most halogens). This data is commonly used to confirm stoichiometry, check alloy composition, or identify and quantify impurities in research and quality control.