What Is Glow Discharge Optical Emission Spectroscopy (GDOES)?
GD‑OES is a technique for elemental compositional analysis and depth profiling of solids. It is particularly well suited for analysis on thin‑ and thick‑film samples, or for depth‑profiling of multilayer film stacks.
The advantages of GD‑OES are short analysis times with minimal sample prep, the ability to measure a wide range of elements simultaneously (including C/H/N/O), fast depth profiling, and the ability to analyze surface and bulk composition in a single measurement.
Wide Element Range
Detects all elements, including light ones (H, C, N, O, Li), across the periodic table.
Fast Multi-Element Profiling
Simultaneous detection for surface and bulk composition with rapid analysis times.
High Depth Resolution
Achieves nanometer-scale depth profiling with ~1 nm resolution.
Why Use GDOES?
Glow Discharge Optical Emission Spectroscopy (GD-OES) is a fast, quantitative technique for elemental composition and depth profiling of solid materials. It enables simultaneous detection of all elements, including light ones like H, C, N, O, and Li—with minimal sample preparation.
GD-OES is ideal for studying thin films, multilayers, and coatings across metals, semiconductors, and ceramics, providing rapid, high-resolution insights that support R&D, quality control, and failure analysis.
Rapid Layer Insight
Delivers fast, accurate compositional profiles for multilayer films and coatings.
Minimal Sample Prep
Requires little to no sample preparation, reducing turnaround time.
Broad Material Compatibility
Suitable for metals, alloys, semiconductors, and ceramics with high repeatability.
Working Principle
In a GDOES measurement, a low‑pressure glow‑discharge (GD) plasma (typically Argon) is used to sputter away the surface of the sample being measured. As material is sputtered from the surface, the high‑energy plasma induces subsequent fluorescence events characteristic of the elements in the plasma. These photons are detected by an optical emission spectrometer (OES).
The intensity (for a given emission line) is proportional to element concentration in the ionizing plasma. Time can be correlated to depth from a sample’s surface, enabling depth profiling and quantitative compositional analysis.
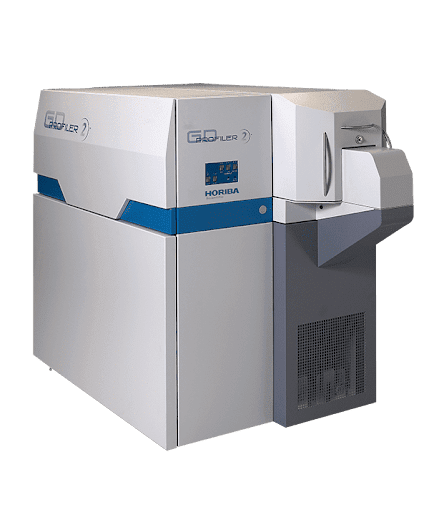
Equipment Used for GDOES:
Covalent’s GD-OES capability is powered by the GD-Profiler 2 pulsed RF Glow Discharge Optical Emission Spectrometer, enhanced with Differential Interferometry Profiling (DiP). This system delivers ultra-fast, high-resolution depth profiling across thin and thick coatings, with nanometer-scale precision in erosion depth measurement. It supports all elements from trace to bulk, handles both conducting and insulating materials, and includes advanced optical detection for high dynamic range and simultaneous multi-element analysis, which is ideal for multilayers, interfaces, and bulk composition studies.
GD-Profiler 2 pulsed RF Glow Discharge Optical Emission Spectrometer
- Spectral Range: 120 nm to 800 nm.
- Simultaneous measurement: Of all elements, including light elements H, C, N, O, F, L.
- Spot Size: 2 to 8 mm.
- Depth resolution: As low as ~1 nm.
- High Dynamic Detector with industry-leading integration times and linear dynamic acquisition range (5 x 109).
- Plasma Sputtering Ion Energy: 50eV.
- Pulsed Plasma Gas Ion Frequency: 13.56 MHz RF.
- Anode Tube Diameter: 4mm.
Key Differentiators
| Property | GDOES |
|---|---|
| Spectral Range | 120 to 800 nm |
| Elements Measured | Full periodic table including light elements H, C, N, O, F, Li |
| Spot Size | 2 to 8 mm |
| Depth Resolution | ~1 nm |
| Plasma Sputtering Ion Energy | 50 eV |
| Pulsed Plasma Gas Frequency | 13.56 MHz RF |
| Anode Tube Diameter | 4 mm |
| Measurement Capability | Surface and bulk composition, multilayer depth profiling |
| Strengths | Fast profiling, minimal sample prep, nm-scale depth resolution, wide dynamic range |
| Limitations | Less sensitive than GD-MS, external calibration is needed, and high-energy sputtering may cause light element diffusion |
| Sample Requirements | Solid, flat, smooth, or rigid materials; conductive preferred; insulating possible with care |
Strengths
- Wide dynamic range (ppm to wt%).
- Full periodic table.
- Excellent depth resolution (nm-scale).
- Fast depth profiling.
- Minimal sample prep.
- Great for quickly profiling complex layered materials.
Limitations
- Less sensitive than GD-MS.
- Elemental concentration and depth scales both need external calibration.
- High-energy sputtering may cause diffusion of light elements, limiting accuracy.

Sample Information
The depth profile of a CuInGaSe Solar Cell shows how GDOES can be used to extract quantitative compositional information as a function of penetration depth into a sample after some additional analytical steps are performed (as described in this application note).
From:
Horiba
What we accept:
- Solid, flat, smooth, or rigid materials.
- Conductive materials are preferred for optimal performance.
- Insulating materials can be analyzed, but may pose additional challenges.
Use Cases

Metallurgy
Verify the composition of alloys and measure the thickness of oxides or coatings, supporting routine quality control operations.

Aerospace & Composites
Determine the thickness and chemical composition of coatings.

Photovoltaics
Determine the thickness and chemical composition of multilayered materials and assess interface quality and interdiffusion.

Energy & Battery Manufacturing
Use depth profiling of electrodes to assess the depth of lithiation.

Consumer Electronics
Identify and quantify impurities in specific regions or layers of printed circuit boards (PCBs).
Complementary Techniques
- GD-MS: Offers better sensitivity for most elements than GD-MS, but is generally limited to bulk analysis.
- ICP-OES/MS: Provides quantitative bulk elemental analysis. Often used to calibrate GDOES methods for quantitative depth profiling.
- SEM-EDS: Surface and near-surface chemical analysis. Non-destructive alternative to GDOES for surface chemical composition. Limited ability to measure light elements like H and Li.
- XRF: Faster, simpler, non-destructive, but with lower sensitivity and less surface-specificity than GDOES. Limited ability to measure light elements.
Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS)
Measures trace elements with high accuracy. Explore
Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy (ICP-OES)
Quantifies multiple elements at very low concentrations. Explore
Why Choose Covalent for Your GDOES Needs?
Frequently Asked Questions
Identifying the right test can be complex, but it doesn’t have to be complicated.
Here are some questions we are frequently asked.
What types of materials can be tested with GDOES?
GDOES can analyze most reasonably hard, flat materials, including metals/alloys, semiconductors, ceramics, and certain plastics.
What information does GDOES provide?
When properly calibrated, GDOES provides elemental composition with depth profiling, suitable for characterizing bulk composition, layer thickness, and/or interfacial regions.
How deep can GDOES be analyzed in a material?
GD-OES can reliably analyze ~100um into a material.
Why use GDOES instead of another surface analysis technique?
GDOES provides much faster depth profiling than other techniques like SIMS or XPS. It also has the advantage of capturing light elements like H and Li.
Does GDOES require special sample preparation?
Minimal sample preparation is required for GDOES. Some samples may need to be cut or mechanically polished.
Can GDOES detect light elements like hydrogen or lithium?
Yes, H and Li can both be measured by ICP-MS.
How long does a typical GDOES test take?
Once the tool calibrated and a method developed, a typical GDOES measurement only takes a few minutes.