What Is Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR)?
Attenuated Total Reflectance – Fourier Transform Infrared (ATR-FTIR) Spectroscopy is a rapid, non-destructive technique that identifies a material’s chemical composition, structure (functional groups), and optical properties. This form of Fourier Transform Infrared spectroscopy is primarily for surface and bulk chemical compositional analysis across industries where speed, reproducibility, and minimal preparation are essential.
Versatility
Applicable to both solid, semi-solid, and liquid samples.
Zero Sample
Preparation
Measures output spectra with minimal to no sample preparation or dilution.
Broad Applications
Applicable across pharmaceuticals, materials science, forensics, and environmental analysis.
Why Use ATR-FTIR?
ATR-FTIR analysis is versatile and requires little or no sample preparation, making it ideal for rapid chemical composition analysis. It can handle solids, liquids, pastes, and water-based solutions that are challenging for other infrared methods. ATR-FTIR spectroscopy also allows real-time monitoring of reactions and surface-level changes without altering the sample.
Non-Destructive Testing
Preserves sample integrity while enabling accurate measurements.
Accurate Surface Chemical Analysis
Penetrates only a few microns for coatings, thin films, and near-surface interactions.
Real-Time Monitoring
Tracks chemical reactions and changes as they happen.
Working Principle
Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier Transform Infrared spectroscopy relies on a specialized ATR crystal with a high refractive index. In ATR-FTIR analysis, infrared light is bounced through the crystal in contact with the sample. The light forms an evanescent wave that penetrates just a few microns into the surface, interacting with the material.
The absorbed light corresponds to the vibrational modes of a sample’s chemical bonds thus, producing an FTIR spectrum with peaks that correspond to functional groups unique to the sample. ATR-FTIR spectroscopy helps identify compounds, examine optical properties, monitor reactions, and assess material composition in the pharmaceuticals, materials science, forensics, and environmental testing.
- Diamond ATR crystals are durable and suitable for most materials due to their hardness and high refractive index.
- Germanium ATR crystals provide shallower penetration depth and are ideal for thin films or highly absorbing samples such as carbon black.
Because ATR-FTIR only probes surface layers, it is exceptionally well-suited for thin films, coatings, and layered materials.
Equipment Used for ATR-FTIR:
Covalent's ATR-FTIR analysis is powered by advanced ThermoFisher instrumentation, delivering high-resolution FTIR spectral analysis with flexible sampling modes.
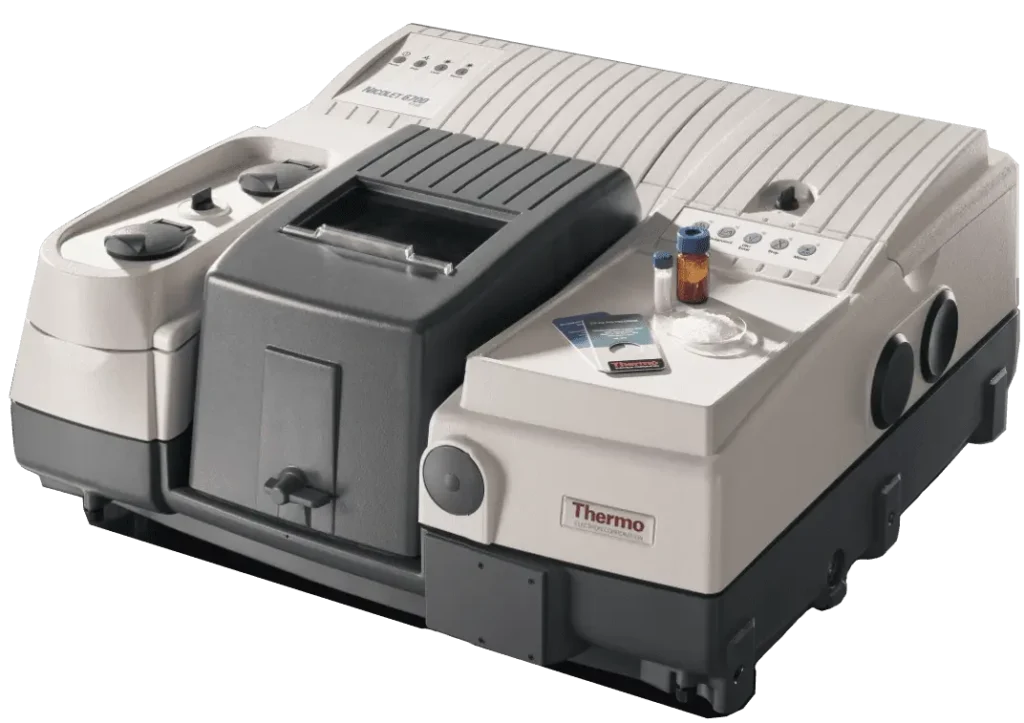
ThermoFisher Scientific Nicolet IS50 FTIR Spectrometer
- Multiple Detectors with Flexible Spectral Range: 7800 to 350 cm⁻¹.
- Mid-IR Optical Resolution: < 0.09 cm⁻¹.
- Wavenumber Accuracy: better than 0.005 cm⁻¹.
- Flexible Analytical Modes.
- Accessories:
- Pressure-controlled diamond ATR (most common).
- High-pressure diamond ATR (for very hard samples).
- Ge ATR (surface identification, carbon black–filled samples).
- Variable-angle ATR (ideal for thin films on substrates).
- Transmission (thin films and KBr pellets).
- Spectral Reflectance (thin films on reflective surfaces or metal coatings).

ThermoFisher Scientific Nicolet Continuum IR Microscope
- 15x and 32x objectives.
- Detector options: Narrow-band MCT-A High performance (4000 to 750 cm⁻¹) and Narrow-band MCT-A (50um element, 4000 to 700 cm⁻¹).
- Sampling modes: Transmission, reflection, Ge ATR, and diamond cell transmission.
- ATR objectives: Dedicated with interchangeable Diamond, Ge, ZnSe, and Si crystals; integrated pressure sensor for robust sampling.
- Grazing angle objective: NA 0.99 for sensitive thin-film and surface analysis.
- Detector configuration: Dual detector bay supporting MCT-A, MCT-B, and InGaAs detectors for broad spectral coverage.

Key Differentiators
Attenuated Total Reflectance FTIR delivers rapid results with minimal sample preparation. It directly analyzes solids, liquids, gels, and powders while maintaining high reproducibility and accuracy in surface chemical analysis. Laboratories use it for both routine checks and advanced ATR-FTIR spectroscopy studies, making it a versatile and reliable technique.
Strengths
- Rapid, non-destructive identification of solids, liquids, gels, and coatings: Ideal for verifying materials and screening unknowns.
- Minimal to no sample preparation: No dilution, slicing, or special handling required.
- Surface-sensitive analysis: Probes a few microns deep to detect coatings, films, and contaminants.
- Highly reproducible spectra: Uses durable diamond or Ge ATR crystals across a wide range of materials.
- Real-time monitoring capability: Enables tracking of reactions or surface changes.
Limitations
- Surface-only sensitivity: Limited penetration depth (0.5-2 µm) means bulk chemistry is not measured.
- Variable quantitative precision: Can be affected by surface irregularities or poor crystal contact.
- Sample constraints: Not suitable for rough or highly absorbing samples without specialized ATR crystals (e.g., Ge).
- Thickness measurement limits: Cannot measure exact layer thickness, only relative trends or composition changes.
- Potential spectral interference: CO₂ or moisture may affect results without proper purging or correction.

Unsure Whether ATR‑FTIR Is Right for You?
Learn how surface‑sensitive FTIR can solve your materials questions.
Sample Information
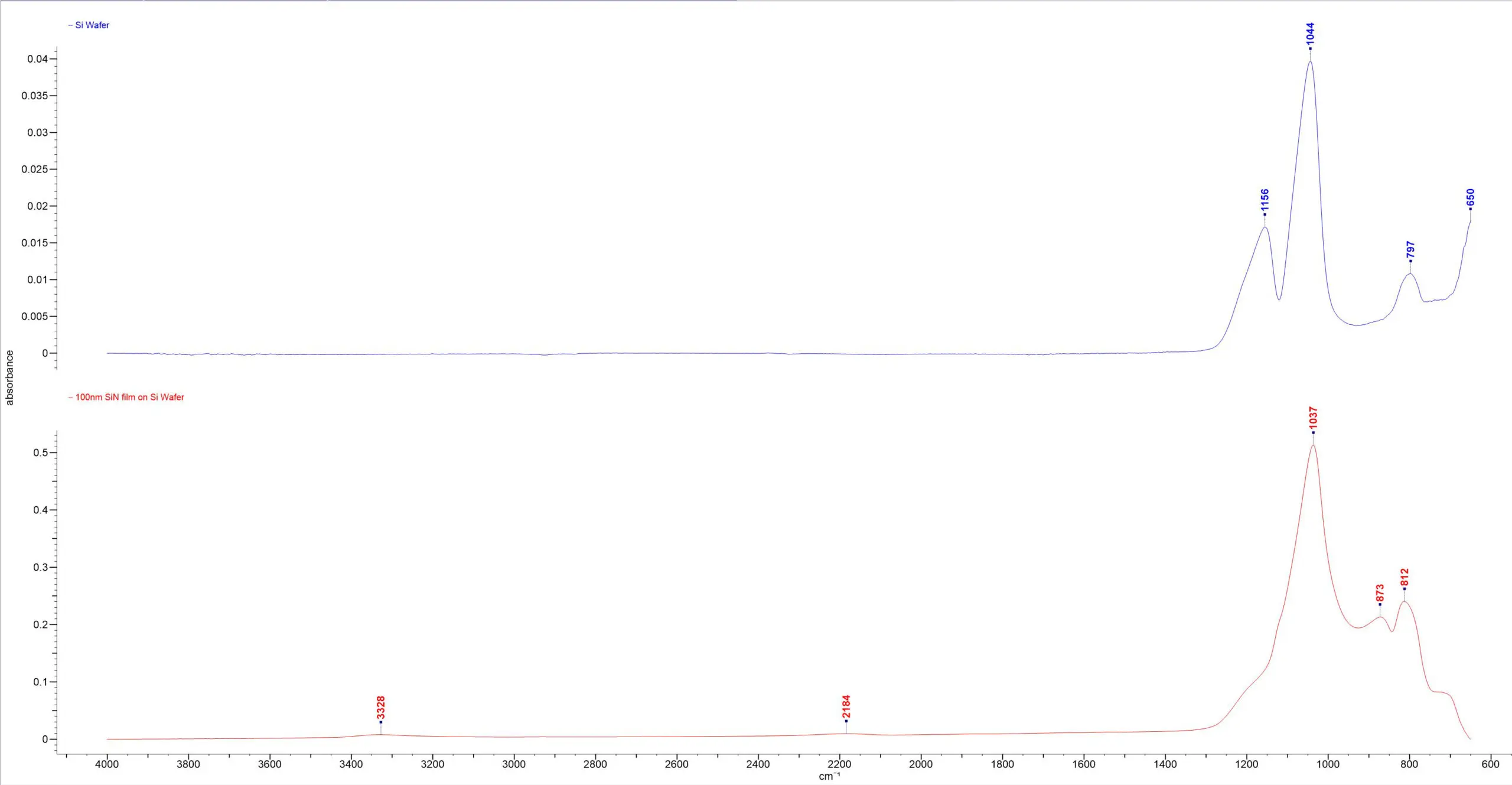
Variable Angle Germanium ATR – Variable Ge ATR: Top: Si Wafer with no coating Bottom: 100nm SiN film Coating on Si Wafer.
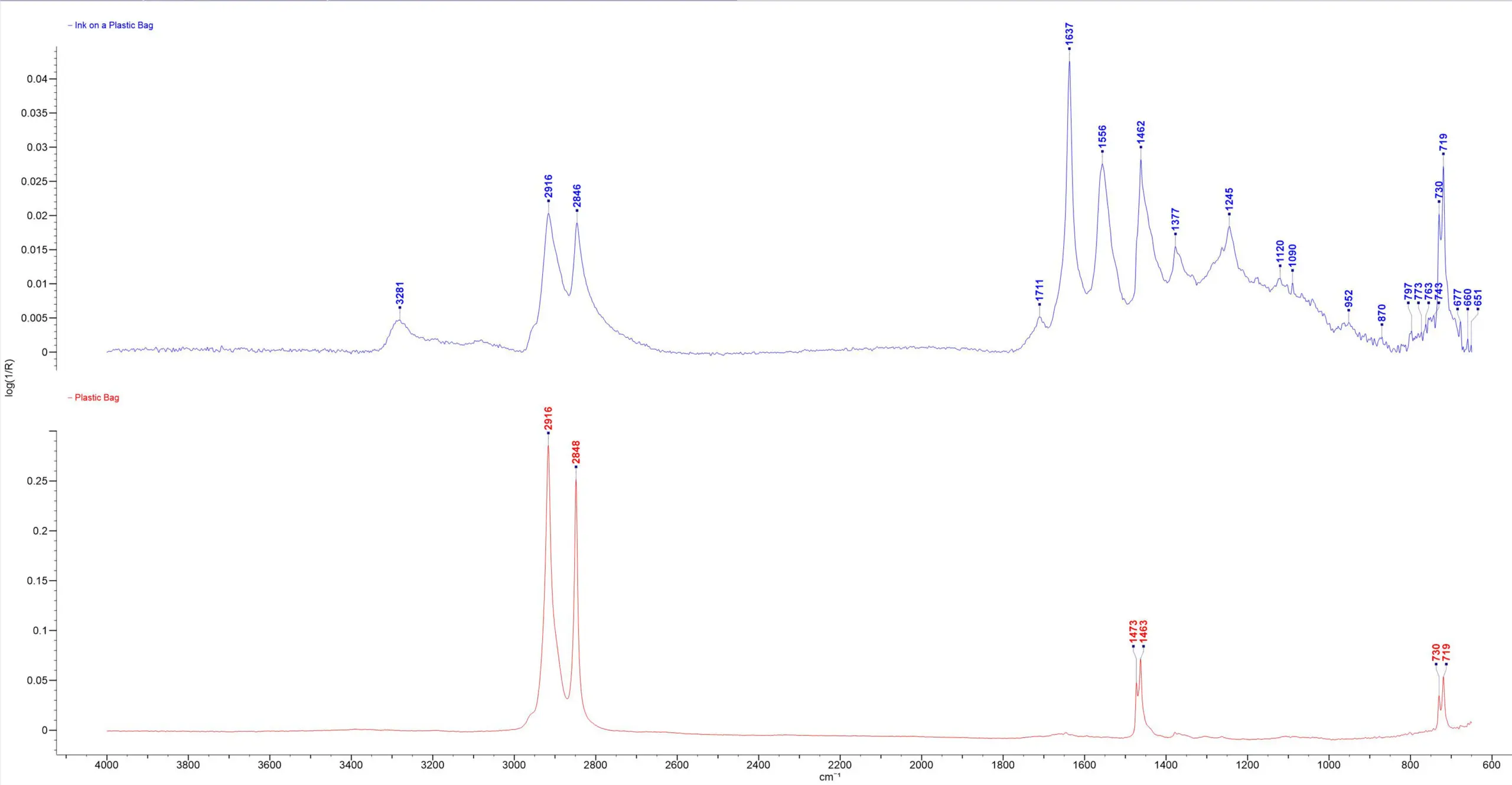
Mircorscope ATR FTIR – uGeATR- polyamide ink on PE bag: Top: dark area on a plastic bag identified as a polyamide ink Bottom: bulk clear plastic bag identified as polyethylene.
What we accept:
- Works with solids, liquids, gels, powders, and coatings.
- The best results are when the sample covers the ATR crystal (>1 mm in diameter).
- Microscope mode enables analysis of small areas down to 20 µm.
- The maximum sample size height for micro ATR-FTIR services is ~20 mm.
Use Cases

Electronics
- Identifying unknown residues on printed circuit boards (PCBs).
- Detecting contamination on metal pins, plates, or coatings.
- Comparing good vs. bad material lots for quality assurance.

Aerospace
- Surface analysis of coatings and thin films on components.
- Monitoring degradation in polymers or composite materials.
- Confirming raw material identity and batch consistency.

Polymers & Materials Science
- Verifying polymer blend composition.
- Assessing surface-level degradation or chemical changes.
- Screening thin films, coatings, and layered materials.

Pharmaceuticals & Biomedical Devices
- Surface chemical analysis of 3D-printed biomedical polymers.
- Rapid identification of active materials and contaminants.
- Monitoring degradation or chemical consistency in formulations.

Energy & Battery Materials
- Assessing surface degradation in electrodes or separators.
- Identifying contaminant residues on energy storage materials.
- Verifying the composition of thin films and coatings.
Complementary Techniques
ATR-FTIR is a strong first-pass screening method, but deeper insights often require additional techniques. At Covalent, ATR-FTIR analysis is frequently paired with methods that extend its reach into molecular, elemental, and trace-level domains.
The commonly paired techniques include:
- GC-MS (Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry): Targets volatile and semi-volatile organic compounds, enabling precise identification of trace additives or contaminants not visible in FTIR spectral analysis.
- NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy): Resolves complex molecular structures, detects additives, and quantifies minor components within mixtures.
- Raman Spectroscopy: Complements ATR-FTIR by capturing vibrational and crystalline structures that may be weak or inactive in FTIR spectra, offering a clearer picture of molecular arrangements.
- SEM-EDS (Scanning Electron Microscopy with Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy): Combines high-resolution imaging with elemental composition, making it ideal for analyzing metals, ceramics, and other inorganic materials.
- XPS (X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy): Provides surface-sensitive chemical information, including oxidation states, elemental ratios, and thin-film composition.
ATR-FTIR Services often serve as the first step in a multi-technique workflow, guiding which complementary methods will provide the most value for complete material characterization.
Energy Dispersive X-ray Fluorescence (EDXRF)
Quick, non-destructive material composition & thickness analysis. Explore
Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)
Identifies and quantifies small organic molecules in mixtures. Explore
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (NMR)
Determines molecular structure, composition, and dynamics. Explore
Raman Spectroscopy
Measures inelastic photon scattering for chemical identification. Explore
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
Images surface topography and composition with electrons. Explore
X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
Measures surface elemental composition and chemical states. Explore
Why Choose Covalent for Your ATR‑FTIR Needs?
Covalent’s ATR-FTIR lab combines speed, accuracy, and flexibility. We analyze solids, thin films, and microsamples with minimal prep with both benchtop and microscope-based systems.
Our scientists bring chemistry, physics, and materials science expertise, ensuring precise FTIR spectral analysis and interpretation. Covalent delivers insights beyond the raw data, from routine screening to advanced surface chemical analysis.
Every project receives individual attention, from method selection to final reporting, so you get the highest value from your FTIR Analysis Services.
Frequently Asked Questions
Identifying the right test can be complex, but it doesn’t have to be complicated.
Here are some questions we are frequently asked.
How does ATR-FTIR compare with transmission FTIR for surface analysis?
ATR-FTIR is surface-sensitive (a few microns deep), while transmission FTIR measures bulk properties and requires thin films.
What crystal types do Covalent use?
We use diamond ATR for durability and germanium ATR for surface-sensitive analysis and strongly absorbing samples.
Can ATR-FTIR detect coatings or layering?
Yes, it can confirm coatings and provide relative thickness trends, but precise thickness measurement requires other methods.
What are the sample requirements?
Samples should cover the ATR crystal (>1 mm). Microscope ATR-FTIR spectroscopy can analyze down to 20 µm.
How deep does ATR-FTIR penetrate?
Typically 0.5–2 µm, depending on wavelength, crystal, and contact quality.
Which industries use ATR-FTIR?
Electronics, aerospace, polymers, pharmaceuticals, and energy storage use ATR-FTIR services for surface chemical analysis and contaminant detection.
What is the turnaround time?
Standard ATR-FTIR analysis reports get delivered in 5-7 business days, with expedited options available.
Can ATR-FTIR provide quantitative data?
Yes, while ATR-FTIR is inherently qualitative when combined with chemometrics or multivariate models, it can quantify additives, blends, and degradation states.
What are common spectral interferences?
Atmospheric CO₂ and water vapor can interfere, but purging and baseline corrections help mitigate this interference.
How reproducible are the results?
ATR-FTIR provides highly reproducible results across instruments when proper calibration and contact are maintained.